EP03: 📚VPC Tutorials & Reads – Curated guide to master AWS networking, security, and cost optimization.
In my last episode, we explored advanced IAM. This week, we’re diving into VPC—your private network in AWS—and uncovering how to design, secure, and connect cloud networks like a pro!
📚What I'm Reading this Week
https://medium.com/@fedi.mbarki/downgrading-amazon-eks-a-workaround-for-an-unsupported-operation-8b24aba43b92
https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/whats-new/2025/08/aws-billing-cost-management-customizable-dashboards/
https://benchling.engineering/how-we-run-terraform-at-scale-da7bb75dc394
A few years ago, I assisted a startup in migrating from its on-premises setup to AWS.
Everything looked smooth, servers were up, load balancer configured, security groups wide open, yet the application wouldn’t connect to the database.
Hours passed, frustration grew, and people started blaming AWS.
The reality? The mistake was ours.
The database sat in a private subnet with no NAT or route to the app’s subnet.
In short, we had built a “data center” with locked doors and forgot to keep the keys.
That’s when it clicked — a VPC is like your personal neighborhood inside AWS. You decide:
where the streets (subnets) go,
how traffic flows (route tables),
Who gets to use the gates (gateways & peering).
Note:- If you don’t plan it right, you’ll either lock yourself out or leave the main gate wide open.
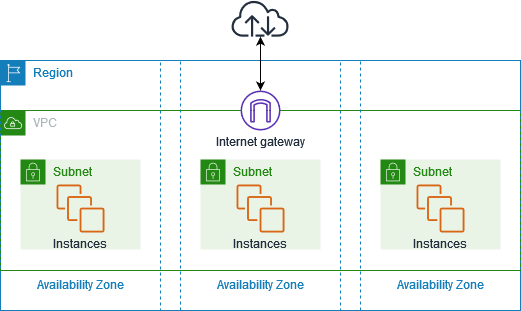
🏗️ What is a VPC?
Imagine AWS giving you an empty plot of land.
On this land, you build your own private data center that’s your VPC (Virtual Private Cloud).
Key Components of an AWS VPC
Subnets: Logical divisions of a VPC that map to specific Availability Zones, used to organize and isolate resources.
IP Addressing: Supports IPv4 & IPv6; you can assign AWS-provided or bring-your-own IPs to resources like EC2, NAT, or Load Balancers.
Routing: Route tables define how traffic flows within the VPC and to external networks.
Gateways & Endpoints:
Internet Gateway → connect VPC to the internet.
NAT Gateway → allow outbound internet access for private subnets.
VPC Endpoints → private access to AWS services without internet exposure.
VPC Peering: Direct communication between two VPCs without using the internet.
Transit Gateway: A scalable hub that simplifies routing between multiple VPCs, VPNs, and Direct Connect.
Traffic Mirroring: Duplicate traffic from network interfaces for monitoring & security analysis.
VPC Flow Logs: Capture IP traffic details for auditing, troubleshooting, and monitoring.
VPN Connections: Secure tunnels to connect on-premises networks with your AWS VPC.
In short: A VPC is your isolated, controlled cloud “data center.” You decide how systems talk to each other and to the internet.
The diagram is from AWS's official
💡 VPC Notes – Costs & IPs
VPC is free → You only pay for extras like NAT Gateway, IPAM, traffic mirroring, analyzers, and public IPv4s.
Private IPs are free → Public IPv4s (EIP, EC2 Public IP, BYOIP) cost money.
Default VPC → AWS services (ELB, RDS, EMR) run here if you don’t create custom VPCs. Public IPv4s in it are billed.
Free Tier → 750 hours/month of EC2 public IPv4s free; beyond that, normal charges.
Connecting Your VPC
Public subnets → Internet Gateway
Private subnets → NAT Gateway
VPC-to-VPC → Peering or Transit Gateway
On-prem → VPN or AWS Direct Connect
🔐 Security & Monitoring
Security Groups & NACLs: Act as virtual firewalls to control inbound and outbound traffic.
VPC Flow Logs: Capture information about the IP traffic going to and from network interfaces in your VPC.
Traffic Mirroring: Copy network traffic from network interfaces and send it to security and monitoring appliances for deep packet inspection.
AWS Network Firewall: A managed service that provides network traffic filtering and intrusion prevention at scale.
📈 Real-World Use Cases
Hybrid Cloud: Connect your on-premises data center to AWS using VPN or Direct Connect.
Multi-VPC Architectures: Use Transit Gateway or VPC Peering to interconnect VPCs across accounts or regions.
Secure Internet Access: Use NAT Gateways and VPC Endpoints to control internet access for private resources.
Service Integration: Connect to AWS services like RDS, ECS, and S3 within your VPC using private or public access, depending on your architecture.
🧠 Best Practices
Plan Your IP Addressing: Avoid overlapping CIDR blocks to ensure smooth connectivity.
Use Private Subnets for Sensitive Resources: Keep databases and application servers in private subnets to enhance security.
Monitor Network Traffic: Use VPC Flow Logs and Traffic Mirroring to keep an eye on network activity.
Automate Network Infrastructure: Use tools like Terraform or AWS CloudFormation to manage your VPC resources.
💼 Interview Corner – VPC Special
Test your VPC knowledge with these scenario-based questions:
Private Subnet Internet Access:
You have a private subnet that needs to download software updates from the internet.
Ques: Which VPC component would you use and why?Cross-VPC Communication:
Two VPCs in different AWS accounts need to communicate privately.
Ques: How would you set it up? Transit Gateway or VPC Peering? Explain the pros and cons.Hybrid Cloud Setup:
Your on-premises data center must access an AWS VPC securely.
Ques: Which connectivity option would you choose and why—VPN or Direct Connect?Cost Optimization:
A developer accidentally routes all S3 traffic through a NAT Gateway, increasing the bill.
Ques: How would you prevent such misconfigurations in the future?Security Troubleshooting:
An EC2 instance in a private subnet cannot reach an RDS instance in another subnet. Security groups are properly configured.
Ques: What VPC components and route configurations would you check?
📌 Key Takeaways
VPC = Your private network in AWS — control your own isolated cloud “data center.”
Subnets, IGW, NAT, Route Tables = Control & Security — define who can go where and how traffic flows.
Peering & Transit Gateways = Hybrid & Multi-VPC Connectivity — easily connect VPCs or on-premises networks.
Monitoring & Automation = Stay Ahead — use flow logs, alerts, and automation to prevent misconfigurations.
IP Planning = Avoid Surprises — assign and track IPv4/IPv6 carefully to reduce conflicts and unnecessary costs.
📚 Deep Dive: VPC Tutorials & Reads
📘 New Book: Practical FinOps
A hands-on guide born from managing thousands of cloud accounts and petabytes of data—tracking real-world successes and costly mistakes.
📚 Grab early access at 50% off: link
😂Meme of the week:
📬 Get in Touch
What’s been your trickiest VPC challenge—subnet design, route tables, peering setups, or NAT/IGW configs? Reply and let me know, I’d love to feature your stories in the next issue.
If you enjoyed this, drop ❤️ and share! If you want to collaborate or sponsor the newsletter, email me at pranjalikomal5@gmail.com.
See you next time! Until then → design smart, deploy secure.
— Pranjali, DevOps & Cloud Consultant ☁️
Thanks for reading! If you have not subscribed yet, you can subscribe here.